Multi-storey apartment buildings occupy more and more specific gravity in the practice of housing construction. Their use makes it possible to significantly increase the number of apartments in a house, increase the building density of cities and towns, which helps reduce the built-up area. The latter is of great importance, since the expansion of urban areas aggravates the transport problem and leads to higher prices. utility networks, increases the distance between housing and places of work and leisure, which, in turn, reduces a person’s free time.
However, it is interesting to note that almost none of the apartments built represented innovation in the way of organizing internal space, with the exception of some examples of housing of social interest. In a certificate of classification of Brazilian modernist buildings, Bruand says that building specialists had a wider scope available to them in the execution of buildings.
There would, however, be a disproportion between the social achievements, whose sheds were very minor and gave birth to only a few valid attempts - Pedreguglio, Gavea, etc. - achievements for the intermediate classes, more abundant but without much interest, and luxury houses or apartments that dominate the market in quantity and quality. This last series is what we have looked at more fundamentally, for obvious reasons: it formed the dominant part of most architects' work, and in many cases the part in which they were able to express themselves better.
In the practice of construction and design of small and medium-sized cities and towns, 4- and 5-story multi-apartment residential buildings are common; large and largest cities are characterized by 9- and 12-story buildings, as well as high-rise buildings (17...25 floors) and high-rise buildings. (over 25 floors). The term “high-rise building” defines the concept of a building that exceeds the height available for extinguishing a fire from mechanical ladders, which allow a mass version to reach a height of 28 m, and a special version - 50 m. The efficiency, structure and shape of multi-story buildings are determined by the type of space-planning building solutions and rational choice of load-bearing structural scheme.
However, its status as a symbol of modernity and social success does not stimulate in its idealizers more reflection on the recent transformations that society has undergone, and, inevitably, we see in these apartments the organizing principles of a traditional isolated house: waterproofness between rooms, between areas, between circulations. Broin also notes that, in general, there is no new research, for example, in Le Corbusier's housing division in Marseille; it is simply a duplication of residences, in an incredibly expanded version of a building that was very much in vogue in Europe of the century.
Multi-storey residential buildings are designed and built with sections, corridors and galleries.
A common design scheme for multi-storey 9- and 17-storey buildings are multi-storey large-panel buildings. In high-rise buildings, a frame-and-stem design is used. The shaft shaft contains staircase-elevator units and vertical engineering communications. A volumetric shaft-shaft is usually erected from monolithic reinforced concrete in sliding formwork. Best layout is achieved in cases where the shapes of the trunk and the building plan are similar. If the building plan is round, the shaft is cylindrical; if it is triangular, it is a triangular prism. With an elongated plan, two shafts are built.
Not surprising, since both models had exactly the same speculative purpose, with the difference that now, property is condoned rather than concentrated in the hands of a single owner. Figure 14 - Olivio Gomes Building, Bahia Calle Sergipe Calle, Sao Paulo, Rino Levi.
However, we realized that there is a desire, albeit nascent, to make spaces flexible in some projects. This can be seen mainly in the work of Rino Levi in most of his apartment buildings, when we noticed the presence of light and, in some cases, mobile partitions in rooms that allowed different types use.
For multi-storey buildings great value acquired by the organization of fire prevention measures. In houses of corridor and gallery types with a height of ten or more floors, common corridors or galleries must have exits to two smoke-free staircases with a floor living area of more than 300 m2. In houses up to ten floors with a living area of more than 300 m2, one staircase is allowed; At the same time, at the ends of corridor buildings, for fire safety purposes, common balconies should be provided for all apartments, connected by external evacuation stairs to the floor level of the fifth floor.
At this time, the main direction of the real estate market will be production large buildings, intended for the wealthier classes. Miniatures, which meant a more economical program, appear to be losing more space in the area of incorporation and the condominium system, so it is in vogue. In this context we can see some differences. This program included the cheapest apartments - with small areas and suppressed rooms - and larger ones - which were full. However, in these decades there are still spacious apartments that are significantly larger than in the coming decades.
Multi-storey buildings of corridor and gallery type must have at least two evacuation stairs. With an increase in the number of storeys, the role of wind loads increases, which, during calculation and design, determine the corresponding volumetric-spatial solution of the building and its architectural and planning structure; the solution of vertical transport, staircase-elevator units and utility systems becomes more complicated; the degree of fire safety requirements is increasing, affecting the layout of internal communications, the choice of types of stairs and elevators, and the standardization of the distance to them from each room; noise from pipelines, garbage chutes, and elevators increases. Therefore, when designing buildings, this entire range of issues should be addressed.
During the previous decades this cosmic organization can already be seen, but presenting some variations of the areas. The most interesting thing is that we can identify it as apartment buildings, created by purely market interests, and in excellent examples of signed production.
This fact may suggest the current difficulty of adopting bold and differentiated proposals for the real estate market in São Paulo and the distance of the creative architect from vertical collective production. B. “Rino Levi Apartments: Real Estate Production, Innovation and the Modernist Promotion of Vertical Buildings in the City of São Paulo.”
In multi-storey buildings, the organization of evacuation routes becomes important. In buildings up to five floors high, one escape route is provided through a staircase located in a fireproof staircase with natural light.
In 9-story residential buildings(sectional) all apartments have one exit to the emergency staircase. In apartments located above the fifth floor, there are also transitions along loggias and balconies to the adjacent section or exits to an external evacuation staircase. In 9-storey corridor and gallery buildings with a living area of more than 300 m2, exits from the corridors and galleries must be arranged with at least two evacuation staircases. In buildings over ten floors, a smoke-free staircase is required.
Metropolis and urbanism - São Paulo summer doctoral dissertation. Architecture and the city in the works of Rino Levi. op. An in-depth understanding of this process will allow us to extrapolate the limits of this work. In some cases the utilization rate was up to 22 times, as in the case of the Martinelli building.
Due to the need for a specific collection and analysis methodology, so-called social interest apartments are beyond the scope of this work. Lecturer at the Faculty of Architecture, Urbanism and Design at the Federal University of Uberlandia. The construction system has successfully passed countless seismic tests and provides the highest standards of resistance to earthquakes, wind and snow, as well as to all loads and overloads envisaged current legislation. Mainly suitable for construction multi-storey buildings three floors above the ground. The high strength and rigidity of the wall panel allows the implementation of unconventional and futuristic architectural forms. Mainly suitable for the construction of single-story and multi-story buildings up to 3 floors. Isolated wall panel made using different types of insulating materials depending on the climate. The construction system has been tested to provide the highest standards of earthquake resistance, wind and snow loads and under all loads and overloads required by current legislation. Architectural design plan and free façade. . With 13 floors and 10 apartments of 144 m² each - one per floor - the building, located in the Itaim Bibi district, in São Paulo, explores its façade perforated panels made of wood and visible reinforced concrete.
Smoke-free staircases are organized by introducing an air zone on the way to the evacuation staircase (to eliminate smoke in the stairwell) or by installing an open or semi-open staircase located outside the contour of the external fences (walls) of a residential building. At closed staircases smoke-free staircases are ensured by air pressure with stimulating exhaust of smoke from staircases, airlocks and halls through ventilation ducts and shafts with valves and self-closing doors on each floor. The valves are opened and the fans are turned on automatically by special smoke detection sensors.
Gallery houses, in which entrances to apartments are made from unglazed galleries leading to staircases and elevators, are typical for housing construction in the southern regions
The idea is to provide maximum thermal comfort for the interior of the apartment. To achieve this, residents can regulate the ambient temperature by moving the panels present on the northern and eastern facades, providing more or less shade depending on the frequency of the sun when necessary, explains Marco Kogan, author of the project.
Another feature studied by the architects is that the panels are perforated, which reminds them. With a checkered pattern and small holes, the leaked elements allow the breeze to enter, making the interior much cooler and more pleasant.
3.3 Space-planning solutions for sectional houses
Sectional residential buildings consist of residential sections, each of which has a common vertical communications unit (staircase and elevator) for a group of apartments united by floors. A section is a part of a residential building with apartments served by a single staircase.
Sections within a floor are designed with two, three, four, six and eight apartments or more. Large quantity apartments in a section provide the most economical use of vertical communications, however, three- and four-apartment sections have greater urban planning flexibility. In climatic regions III and IV, in order to ensure cross ventilation, it is permissible to use sections with two apartments per floor with a total area of 150... 200 m2.
The rate of land consumption for driveways and approaches will be
With a strong reference to the Brutalist buildings featured in the 20th century metropolis of São Paulo, the visible concrete is made of ribbed wood and makes up the south and west façades. It is a strong element that stands out in the chosen traditional construction system. Present in large gables, the texture of these lattice panels offers a beautiful and poetic effect when illuminated by the sun. All facades in the building appreciate the materials used. There is no paint, and the coloring is characteristic of apparent materials.
There are ordinary (middle) sections and end sections with or without windows at the end, corner ones with different numbers and composition of apartments, limited (meridional), partially limited and unlimited (latitudinal and meridional) orientation, which provides different urban planning maneuverability of residential buildings. The location and composition of apartment sections in projects have a digital designation (the number of living rooms in the apartments) and a letter designation (the location of the section in the house plan - row, end, corner). For example, the designation T.2-3-3 characterizes a three-apartment end section with two- and three-room apartments etc.
To control sunlight and ensure thermal comfort, muxarabiz is distributed throughout the building in accordance with the existing insolation. Panels with checkered perforations also allow air to pass through, making homes shaded, ventilated and naturally pleasant. Another feature the architects explored in the panels was mobility. They can be moved to different times day and serve various types use and occupation in apartments. The consequence of this is the formation of several patterns that arise as the Sun moves.
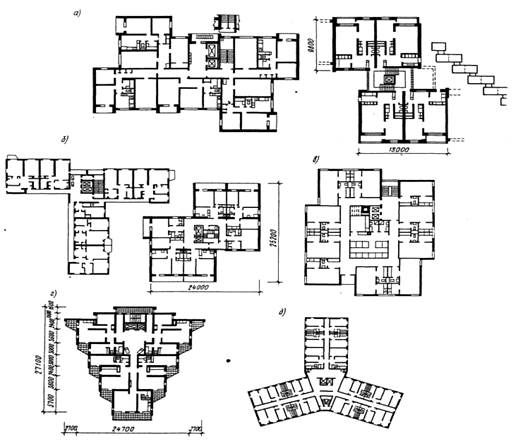
 Compositional diagrams of multi-storey building plans are shown in Fig. 7.2.
Compositional diagrams of multi-storey building plans are shown in Fig. 7.2.
In the architecture of a modern industrial residential building, form formation is closely related to the functional content and, above all, to the structure of sections. At the same time, the main gradations of number of storeys determine a number of features. So, if for nine-story residential buildings a loggia or balcony in each apartment is not necessary based on fire safety requirements, then for 12-story and higher buildings they are required. The structure of the facade is in many cases determined by these requirements.
The wall load-bearing frame is most common in the construction of residential multi-story buildings. All three systems are used: with transverse, longitudinal and cross walls. The predominant construction system is large-panel
Light effects make facades dynamic - a real living facade. On the other hand, the interior of the building receives shadow patterns with a poetic effect. Maximum area plot - 620 m². 045 m² area distributed in a small building compared to large ones modern buildings. The result is friendly relations between the city and its surroundings, says Kogan.
Solutions for entrances, windows, grouping of loggias and the nature of the spot they form, framing of loggias and the walls on which their slabs rest, material, texture and color of the fence, methods of arranging the crowning part are among the main compositional elements of the facades of residential buildings.
The requirements for insolation of premises in the I and II building-climatic regions determine the use of latitudinal sections, located with the longitudinal axis in the general east-west direction, and meridional sections, located with the longitudinal axis in the general north-south direction. Currently, wide four-apartment sections with a set of apartments 2-2-3-3 or 1-2-3-3 are common in design practice.
The configuration of each floor is universal. The plan can be configured as open and modern attic, but it can also be a traditional one-story apartment with two suites. The size and needs of the family determine the plant, explains Caroline.
This model captures only the core and vertical circulation services located near the southwest portion of the building. The solution reduces interference from elevators and stairs in an open plan. There are 13 floors, 10 apartments and maximum integration between interior and exterior, ensured by large glass panels located in the rooms, each of which faces east. One of the apartments is located longitudinally in relation to the facade.
Examples of the layout of latitudinal sections for climatic regions I and II are given in Fig. 7.3.
For meridional houses, the orientation of which is allowed only on two sides of the horizon (east and west), such a restriction does not exist and the apartments in them usually have a one-way orientation. Therefore, meridional sections are used to accommodate six-room apartments (with a total area
The ground floor, raised by pilotism, maintains a strong connection between the internal and external environment through the garden. Realized on a plot of land with an area of just over 1500 square meters, at 919 Ermag Serafina street, opposite Plaza Carlos Gómez and with foundations facing the narrow street Coronel Rodovallo, the 15-storey, 60-storey building of units is a reference to modern architecture adopted in vertical construction and represents forms that break with the conventional , used in buildings of its time.

Free façade, sun protection and "windows" are the "pillars" of modern architecture found in Itatania. Those who live in Itatia are accustomed to the interest generated by the building in which Sister Serafina travels, especially among architecture students who are sometimes seen in groups photographing the famous building, which is currently undergoing renovation. New paint on the façade and the breeze, a structure that a few years ago moved from concrete to aluminum and which now receives a new embrace.

Rice. 7.3 Layout of sectional residential buildings:
a) latitudinal section, b) meridional section for the southern regions, c) section with a wide body for the northern regions.


In nearly four years at the helm of the 102-person condo, Bassan notes that most of the units have remained in the same family, passed down through inheritance. “The residents are proud of the building, their architecture and Niemeyer’s work,” notes the administrator. When the façade and the pilot were overturned by Condepak, residents can reduce part of the property tax and the territorial city, as well as architect and resident Flavio Rolfsen Laurini, one of the first to benefit from a discount on the maintenance of the subdivision.
Living Residents report pride in living in the building. Her relationship with the building is long-standing, beginning with her grandfather, who bought the block on the top floor when the building was still a factory, and then inherited and occupied by Malu's father for more than 20 years. As an adult, she received from her father an apartment of 130 square meters overlooking Carlos Gomes Square, from where she attends an intimate ceremony with presentations in this space and mobilizations that take place across the street in front of the City Hall.
with an area of 250... 400 m2) or more apartments if there are at least two elevators in the section.
In climatic regions III and IV, one-sided orientation of apartments is not allowed, except for apartments ventilated through staircase in climatic region III (see Fig. 5.15), therefore meridional sections are usually excluded for application. Rice. 7.3, c illustrates the solution of a section with a deep body for the northern regions.
The structural and rhythmic layout of sectional buildings as a whole is predetermined by their functional purpose and depend on the types of sections.
Multi-section residential buildings are formed by blocking a number of sections different composition and configuration in accordance with and based on the requirements for the resettlement of families of the existing numerical and demographic composition, as well as the compositional design of buildings and development in general. The choice of the length of houses depends on economic and urban planning requirements.
It is advisable to use multi-section houses with a length of more than 90 m, as evidenced by the development practice of recent years.
The rhythmic construction of extended facades is determined by the parameters of the typological elements - apartments and sections, the cutting of the wall and the location of balconies and loggias. For houses above 16 floors, it is advisable to have no more than two or three sections in length due to the large shading of the area. The width of residential buildings, ensuring compactness of solutions, is appropriate in the range of 13... 15 m for climatic region I, 11... 13 m for II and III and 9...10 m for IV.
Single-section tower-type residential buildings are a structure of floor-to-floor apartments grouped around a single node of vertical communications - a staircase-elevator block. Multi-storey dotted houses are designed to be multi-storey (9, 12, 16, 17 or more floors). This type of residential building makes it possible to increase the density and compositionally enrich the development, improve the hygienic qualities of apartments due to the perimeter of the external walls per unit area compared to multi-section ones. The desire to find economical and expressive solutions leads to a variety of volumetric-spatial solutions for dotted houses with a variety of complicated plan forms.
In Fig. 7.4 shows examples of various planning solutions for single-section 12... 17-story residential buildings, adopted in domestic and foreign practice: three-beam, T-beam, cross, pair-block, etc. Here we see; that the complication of the plan form makes it possible to make a more expedient space-planning solution for a residential building, makes it possible to provide a larger number of apartments on the floor while ensuring the requirements of insolation and compact layout for any orientation of the house, as well as achieving an expressive volumetric composition of the building. However, such a space-planning solution for panel houses requires more complex structures.
rice. 7.4 Options for various planning solutions for single-section residential buildings: a) with a warm staircase and access to an emergency fire escape, b) with a smoke-free staircase surrounded by corridors, c) with a four-sided corridor around utility rooms, d) stepped plan shape, e) trefoil
The cost-effectiveness of a building is largely determined by the rational organization of the staircase-elevator unit. In dotted houses of dissected shape, ventilation of part of the apartments is organized using floor-by-floor corridors through window openings in the end walls.
In conditions of complex development, with a combination of buildings of different heights, extended buildings are mostly assigned the functions of a background.
Dotted houses high-rise buildings are either combined with background ones as rhythmically defined, regularly placed elements of a residential building (usually streets), or play the role of accents.
3.4 Space-planning solutions for corridor and gallery houses
Corridor residential buildings combine a group of single- and two-room apartments, each of which has access to a common corridor - a horizontal communication room, interconnected with vertical communications - a staircase-elevator unit. The length of the corridors is determined by hygiene and fire safety requirements. The length of corridors illuminated on both sides is allowed no more than 40 m, on one side - 20 m. For longer lengths, light breaks-pockets (halls) should be designed, the distance between which should be 20 m, and between the window opening and the hall - 30 m. To improve ventilation and natural lighting of corridors, the technique of mutually shifting parts of a residential building is often used, which at the same time increases the expressiveness of the architectural design of the building. Indicators of the maximum length of corridors (galleries) in multi-storey residential buildings, which are evacuation routes designed in accordance with regulatory fire safety requirements in accordance with SNiP, are given in Table. 7.1.
Ministry of Education and Science, Youth and Sports of Ukraine
OGASA AHI
Department of Architecture of Buildings and Structures
Abstract on the topic:
Multi-storey residential building
Odessa 2013
INTRODUCTION
Creating a comfortable home for a person is inextricably linked with the urban planning situation and the degree of urbanization of the living environment. With the growth of the size of cities and changes in the environmental situation, the nature of the connection between housing and environment" It is necessary to take this into account when creating residential building projects and placing them in a residential area. The choice of a residential building and its development is made taking into account its role in the structure of the residential environment of the area, which determines its height (number of floors), shape (dominants or elements of ordinary buildings), functional and planning solution.
GENERAL PROVISIONS
The architectural space of a home is largely determined by the psychophysiological requirements of the human body. The number of floors of a building, its internal layout, the area and height of apartments, the connection with the natural and urban environment through the windows of premises or through the installation of balconies and loggias - the psychological and physiological aspects of human perception of the environment are important everywhere.
Residential buildings are measured in "dwelling units" or "dwelling cells" per family, and the cell is measured in m2 total area per person. Schematically, these cells are depicted as a square with “light fronts” - four outer surfaces along which they are placed living rooms with its own light openings (windows). If it is necessary to block residential cells, i.e. when combining them through common external walls, the "light front" of the cell is reduced as the number of interlocking walls increases. One of the essential functions of a home is to provide an opportunity for a person in an apartment to communicate with the outside environment. In addition to windows, open spaces around the apartment - balconies, loggias, verandas, terraces - play an important role.
STAGES OF DESIGNING A RESIDENTIAL MULTISTORY HOUSE AND PRE-DESIGN PREPARATION
Construction multi-storey building can be divided into several large stages. These stages imply that all work is performed at the proper professional level, because a multi-storey building is very complex design, and one of the main tasks during its construction is to ensure the safety of residents. Also not inferior in importance is the creation comfortable conditions for people living in the house and ensuring maximum ease of use engineering communications Houses.
The first stage of construction of a multi-storey building is the choice land plot for construction. Moreover, the site selection is carried out in strict accordance with the urban development plan. The easiest way to get a plot of land is in an area of the city where few houses have been built and a number of more residential buildings are planned to be built. In the central part of the city, where there is a high building density, it is much more difficult to obtain a plot.
When you receive permission to develop the plot of land you have chosen, proceed to the next stage of construction of a multi-storey building. This stage will include a geological examination and topographic survey of the site. At this stage it becomes clear how close they pass groundwater, what is it like general condition soil. Based on geological survey data, the need to build a house using special technologies and building materials.
The third stage of construction of a multi-storey building is the actual construction of the house. This is followed by finishing the facades of the house and finishing it interior spaces. The house will need to be connected to heating, sewerage, and water supply networks. The house is provided with telephone communications and power supply cables are connected to it. After completion of construction and finishing works The construction company is putting the house into operation.
During the creation of the project apartment building Issues regarding sufficient insolation (illumination) of premises are resolved, ventilation of the house and its thermal protection systems are provided. Recently, houses have been built whose external walls are insulated using special materials to avoid unnecessary heat loss. In the process of designing an apartment building, the climatic conditions of the region and seismological conditions must be taken into account.
The project also includes a space-planning solution for the house, so that the customer can see at the design stage what the house will be like and make his wishes, of course, taking into account existing design and construction standards. The project of an apartment building must be agreed upon with the architectural and construction authorities of the city, since the construction of such a building is a very responsible and serious undertaking.
When working on the design of multi-storey buildings, the architect tries to take into account both the wishes of the customer and the possibilities that modern buildings offer. building materials and technology. The architect must apply the maximum of his knowledge and experience in design.
When designing multi-storey buildings, not only the quality and properties of building and finishing materials are taken into account, but also the requirements of environmental and sanitary standards, energy efficiency and appearance. It is also necessary to take into account the development prospects of the area where the house is being built.
In the design of residential buildings, the requirements for functionality and convenience of the building play a significant role. The architect must also think about ways to save heat, electricity, water and other resources. Before creating a project, specialists must carry out a complex of pre-design work. These works involve the development of several sketches of the future building and the choice of its exact location. Options are being identified appearance residential building, from which one will then be selected. The service life and quality of construction depend on the correct design of multi-storey buildings. All design calculations must be checked repeatedly.
The building should fit organically into the surrounding architectural landscape, and not look like a terrible monster among the surrounding houses. Modern construction and finishing materials will help the new house fit harmoniously into the surrounding landscape.
MASTER PLAN FOR A MULTISTORY RESIDENTIAL BUILDING PROJECT
Rational and economical use of the earth's surface as a non-renewable resource is the basic rule for any construction in general. It becomes especially urgent in multi-storey housing construction, which arose from the need for multiple (according to the number of floors) removal of usable (living) area from a unit of urban land surface. Therefore, one should carefully (in m2/person) take into account all types of public use of the earth’s surface, dividing them into mandatory and additional. The building density is primarily affected by the required distances between residential buildings:
Fire breaks (at least 6 m between the ends of buildings and at least 20 m between the sides of buildings with windows).
Gaps providing natural light, insolation and ventilation of residential premises and open courtyard spaces (at least two heights of buildings if they are parallel and not less than one and a half heights if they are perpendicular).
When designing driveways and pedestrian paths, it is necessary to ensure the passage of fire trucks:
Passage of fire trucks (width 5.5 - 6.0 m) on two longitudinal sides for residential buildings over 9 floors high and on four sides for single-section tower-type buildings.
The distance from the edge of the passage to the wall of a building up to 10 floors high is at least 6-8 m, over 10 floors - 8-10 m.
The building area (the surface of the earth under the building) and the area of “fire zones” on both sides of the building constitute the mandatory consumption of the surface of the earth for residential development.
The norm for residential development of land consumption per resident is determined as the width of the residential building (~ 12 m) and two “fire zones” (6-10 m each) per length of the facade per 21 people in a typical floor with the norm of the total area of the apartment per person (20 m2/person), number of floors and sizes of staircase and elevator units (llu). Approximately this amounts to:
for 4th floor (llu 3 x 6 m) - 10-12 m2/person.
for 6-8 floors (room 4 x 6 m) - 9-7 m2/person.
for 10-12 fl. (llu 6 x 6 m) - 6-5 m2/person.
for 18-25 floors (llu 8 x 8 m) - 4-3 m2/person.
Driveways and approaches to residential buildings (combined with fire passages) have the following dimensions:
intra-block passages: two lanes of 3.0 m each,
sidewalk width - 1.5 m, turning radius - 5 m;
dead-end driveway to separate buildings: length no more than 150 m, width - 4.0 m, turning areas - 12 x 12 m.
The rate of land consumption for access roads will be:
for 4th floor - 3.0 m2/person.
for 6-8 floors - 4-3 m2/person.
for 10-12 floors - 2.4-2 m2/person.
for 18-25 floors - 1.6-1.0 m2/person.
The rate of provision of urban population with personal vehicles is 300 cars/1000 residents, i.e. 1-1.5 cars per family or apartment. Open parking lots for temporary storage passenger cars should be provided at the rate of at least 25% of the estimated fleet of individual passenger cars in residential areas.
Landscaping of the residential area of the block and courtyard includes areas of boulevards, squares and courtyard gardens. Consumption rate horizontal surface landscaping area is 4 m2/person.
Order work
Need original work?
Our specialists will help you write a paper with a mandatory check for uniqueness in the Anti-Plagiarism system.
Submit your application with the requirements right now to find out the cost and possibility of writing.
