In the article you will learn what a relief valve for heating is, types of blast valve and tips for installing and choosing a relief valve for water.
There are many factors that influence the stability of the heating system. Sudden temperature changes can lead to leakage of connections. To prevent this from happening, in heating system It is necessary to provide for the installation of a protective device.
Such a device is water pressure relief valve or relief valve. Its use is a prerequisite for the installation of heating devices. What is it used for? safety valve. When the heating system starts, the coolant begins to heat up. It begins to expand, increasing in volume. Accordingly, the pressure on the inner surface of the pipeline walls increases and heating devices.
When the pressure exceeds a certain value, depressurization of the joints occurs. This leads to disruption of the system and ultimately to the occurrence of emergency situation. In order to promptly discharge excess water, a safety valve must be installed. Valve functions.
- Timely removal of excess coolant. This leads to a decrease in pressure in the system.
- The safety valve must be able to adjust the maximum pressure at which it opens. When choosing a specific model, you need to take into account the characteristics of the heating system:
- Average and maximum pressure in the system.
- At what distance is the expansion tank located?
- Length of heating pipes.
- Type of heating system. When installing heating devices, two types of valves are used, the operation of which is based on different principles.

Safety valve installation features

Professional installation safety valve in the heating system is to take into account not only its characteristics, but also the operation of the expansion tank. As soon as the latter is unable to expand the internal volume of the pipes, the bypass valve must operate and remove excess water from the pipes.
According to the rules, the relief safety valve for the heating system must be installed immediately after the boiler outlet pipe (in the diagram these are elements 3 and 4). The optimal distance between them is 20-30 cm. For visual control, a pressure gauge is mounted in front of it. Based on his readings, one can determine current state systems.
There are certain rules for installing a safety valve in a heating system:
- Shut-off equipment – valves, taps, etc. – must not be installed in front of the device and the boiler;
- To remove excess water, a drain pipe is installed at the outlet pipe of a correctly selected heating safety valve. It can be connected to a return or sewer pipe;
- In a closed gravity system, the heating safety valve is installed at the highest point.
In addition, you need to periodically check the condition of the mechanism. Spring models are characterized by “sticking” of the plate to the walls of the housing. This increases the maximum opening pressure of the safety valve in the heating system. As a result, if the permissible pressure value is exceeded, the device will not work.
To a greater extent, the latter relates to the operating conditions of the safety valve for heating rather than to the principle of its operation. However, without this, even with ideal installation, the likelihood of incorrect operation of the device increases.
If the number of emergency descents was 7-8 times, experts recommend replacing the valve. This is due to natural wear and tear on the spring and plate.
What to consider when selecting a safety valve in autonomous system heating? Compliance of its technical characteristics with operational ones. It is also important to connect it to the pipe correctly. For this, it is best to use traditional pipe tow. The FUM tape may not withstand the effects of temperature, resulting in a leak.
To better understand the operating principle of the safety valve, it is recommended to watch a video about the design and operation of the spring model:
Types of safety valve:
- Clutch fuses are made of brass. This type is direct-flow, that is, it opens by pressure. This cheap option, but quite reliable. And has simple design: thread on both sides, and rod with gasket.
- Brass fuse with over complex design. Such a valve should be installed in the heating system after the circulation pump. The spring and rod in this design are made of stainless steel. This safety device can withstand temperature regime up to 1200C.
- Check valves- this is a type of safety device that should not allow a backflow of coolant in the heating system if the pressure drops there.
Safety valve selection
The selection of a safety device for the heating system must be carried out by a qualified specialist. Since there are certain rules that were developed and approved by the state technical supervision. You can also calculate the required diameter on websites that sell such devices; they have a special calculator.
The safety valve must be designed for a pressure that is 20-25% higher normal pressure in the heating system.
Burst valve for boiler. Calculation
The calculation of the safety device must be carried out in accordance with the methodology presented in SNiP II-35 “Boiler installations”.
Since manufacturers rarely indicate technical specifications the actual height of the rod lift; in calculation, this parameter is equal to 1/20 of the seat diameter. For this reason, the valve size as a result of this calculation is somewhat overestimated. In any case, after selecting a device, it is necessary to compare the thermal power of the heating system with that recommended in technical description maximum power for the selected size.
![]()
Installation of a safety valve is required to protect the heating system from exceeding the pressure level above the maximum permissible value. For this reason, the calculation of this device should be reduced to calculating the maximum permissible increase in coolant volume and identifying possible sources of excess pressure.
Sources of volume growth can be:
- Overheating in a heat exchange or boiler unit with subsequent vaporization. When vaporizing, a liquid can increase its volume by 461 times, so this factor is the predominant factor when choosing a valve.
- Failure of automatic control of make-up lines of boiler houses and independent heating systems. This may also be a predominant factor in valve selection.
- The coolant, heating up in a heat exchange or boiler unit, increases in volume. When heated, the specific volume increase is from 0 to 100 °C, which is only 4%, so when selecting the size of a device of this type, this is not a fundamental point.
The selected equipment must ensure the discharge of the calculated amount of coolant, according to the most significant factor in the increase in volume.
Water Heater Pressure Relief Valve
For the formation of the article, many thanks to the resources: fb.ru, strojdvor.ru, kotlomaniya.ru
Greetings, my curious readers and subscribers! M. Aleinikov is in touch with you.
Any heating equipment is in some way explosive because it is under pressure. To minimize the level of danger in modern systems various protective systems and devices. The simplest and most common is the emergency pressure relief valve in the heating system. We’ll talk about what this device is, its characteristics and purpose today.
So, a safety valve is needed to protect the heating system from increased coolant pressure. This problem can arise as a result of strong heating of the water in the boiler, especially when using solid fuel units. After the coolant reaches the boiling point and vaporization occurs, this leads to a pressure surge in the system.
And the results can be significant:
- the formation of leaks or ruptures, usually at joints;
- deformation of polymer pipes and fittings;
- boiler tank rupture;
- possibility of closure.
To avoid such situations, you can install one safety valve closer to the boiler on the supply pipeline, since the pressure rise to a critical level occurs here. Many manufacturers install so-called safety kits on their equipment (relief valve, pressure gauge, automatic air vent).
The use of safety valves is not always necessary. For example, if the heat source in the room is a gas or electric boiler. And this is due to the presence of automatic safety and the absence of any inertia. Even when the peak temperature of the coolant reaches the electrical element or gas burner automatically turn off and further heating will stop almost immediately.
IN solid fuel boilers or furnaces with a water circuit, the installation of such a valve is mandatory. Why? Let's imagine: the firewood in the firebox has flared up, and the water in the network has reached the desired temperature. To reduce its heating, we close the access of air to the combustion chamber and the flame will go out. However, the already hot firebox will continue to transfer heat. When the limit values of 90-95 degrees Celsius are reached, steam is generated.
How will the valve help? It will automatically open the outlet for the accumulated steam and release it. The pressure will then drop to the optimal level. Then this path will be closed and work will continue as normal.
As for the safety valve device. There is nothing complicated about the mechanism. The body is made of plumbing brass using hot stamping technology from two cast elements in a semi-solid state.
Safety valve elements:
- adjustment knob
- seal
- frame
- spring
- pressure relief hole
- locking membrane
An important working element is the spring. The exit to the outside is closed by a membrane. And the elasticity of the spring sets the force of pressure on this membrane. The membrane itself in its normal position is located in a seat with a seal, pressed by a spring. The top support for the spring is a metal washer attached to the rod. The stem is attached to a metal handle, which is used to regulate the valve. The diaphragm and sealing components of the valve are made of polymer materials, and the spring is made of steel.
The operating principle of the valve in question is as follows. In normal mode with normal coolant parameters, the membrane blocks the entrance to the inner chamber. If a situation arises when the pressure in the system increases, the steam-water composition puts pressure on the membrane. At some point, the pressure force of the coolant overpowers the elastic force of the spring, opens the membrane, entering the chamber and then out through the side hole.
After a certain amount of water leaves the system, the pressure will drop and will not be able to withstand the elastic force of the spring and the membrane will return to its original position. If such situations with increased pressure in the system occur periodically, or rather, often, then over time the blast valve loses its tightness and begins to leak.
If you find fresh traces of leakage from the safety mechanism, then you should pay attention to the operating mode of the heat generator.
How to choose the right valve.
The fact is that there are manufacturers who indicate the maximum pressure value, for example, 2 or 3 Bar. The best option would be to have a pressure regulator with a certain range. Moreover, these limits should include the parameters of your boiler.
Next, select the equipment according to the strength of the thermal installation. Just carefully look at the manufacturer's instructions, which indicate the limits of the thermal power of the units with which a valve of a certain diameter can operate.
Never install shut-off valves within the pipeline from the boiler to the location where the pressure relief valve is installed. It is also prohibited to install the device after the circulation pump (it will not be able to pump the steam-water mixture).
If you want to avoid splashing water around the room, you should attach a tube to the outlet of the valve to drain water into the sewer. Or another option: you can install a special funnel with a visible break in the jet on a vertical section of the pipe - this will allow you to visually observe the process.
When purchasing a safety valve for a heating system, decide on its diameter. In no case should it be smaller than the supply pipe, otherwise the hydraulic resistance will not allow the mechanism to perform its functions efficiently.
During installation, the valve of the heating system is placed at an angle towards the boiler, which will allow achieving minimal hydraulic losses when acting on the plate.
Types of safety valves:
a) according to the method of removing excess coolant:
- open type - operate without the use of back pressure and discharge excess liquid outside the system
- closed - the coolant is discharged into the pipeline
b) by capacity (to what height does the spool rise):
- low-lift - the lifting height of the spool corresponds to 0.5 of the seat diameter. As a rule, they are used where HD is a liquid working medium and does not require significant throughput;
- full lift - lift height above 0.25 saddle diameter. They are used in systems with a gaseous medium and open to the full stroke of the spool. May be with manual device for opening or without it.
c) in addition:


I’ll go into a little more detail on latest form safety valves, maybe someone has not encountered them in practice. Their device has three holes - two at the outlet and one at the inlet. The flow of the coolant is determined by a damper in the form of a rod or ball. With the help of rotational movements, the flow of moving fluid is redistributed.
The scope of application of three-way valves is wider, since they are used in cases where several different heating systems operate from one heating boiler. An example would be underfloor heating and radiators.
The three-way valve performs several functions simultaneously:
- divides the plots
- breaks down the flux density by area
- with its assistance, the coolant from the supply and return is mixed until the latter is sent to the underfloor heating system. This means that water will flow into the floor system at a lower temperature than into the radiators.
The higher the initial pressure, the faster the device should operate. In any case, the adjusting mechanism must be protected from direct contact with hot water. After a long period of inactivity, the spring may “stick”, so the device must have a mechanism for testing its performance - a rod for manually retracting the spring.
Take seriously the issue of choosing and installing a safety valve and protect your heating system.
Sometimes unpleasant circumstances arise when the heating system malfunctions and the pressure begins to fluctuate. If the pressure is not regulated, the consequences can be dangerous. To prevent this, the heating system and supply system hot water should be equipped with safety valves. What they are and how they work – we will tell you in this material.
Safety valve in the heating system performs protective function in order to prevent high pressure. This is especially important for steam boilers.
Blood pressure rises most often due to the following reasons:
- refusal automatic systems pressure adjustment;
- sudden increase in temperature environment and the appearance of steam.
Safety products are mainly of two types:
- spring;
- lever-load.
In lever-load structures, the action of pressure on the spool is counteracted by a load, its force is transmitted through the lever to the rod. It moves along the length of the lever, and in this way you can regulate the force of pressure of the spool against the seat. Then it opens when the working environment begins to put pressure on bottom part the spool with a force greater than the force of the lever pressure and the water leaves through the pipe.
And the spring safety units work using an electromagnetic drive. A spring exerts pressure on the spool rod, and adjustment occurs by changing the degree of compression of the spring.
Small heating systems are best combined with spring products; their advantages in this case are as follows:
- compactness;
- the setting can only be changed when using the tools;
- the spool rod may have different positions;
- Possibility of combination with other products.
According to the principle of operation, safety valves are divided into the following:

A direct-acting safety valve can open only under pressure from the working medium, while an indirect safety valve can open only under the influence of a pressure source.
And according to the type of lifting the constipation, the devices are:
- low-lift;
- medium-lift;
- full lift.
Manufacturing materials
Safety products can be made from the following materials:
- brass;
- steel;
- galvanized steel;
- stainless steel
Features of the mechanism and design
The safety brass coupling valve for the boiler is threaded on both sides and has a gasket on the inlet side. The mechanism is spring-loaded. External pressure can increase the blockage. After assembling the structure, it is pressurized, so this type of valve is very reliable and affordable.
Safety shut-off valve also can work in sewer system to protect against backflow pressure.
Features of three-way valves
The purpose and operating principle of three-way safety valves is somewhat different from other options, and so their key differences:

Such valves are most often used in heating systems that include “warm floors”. In this way, the water for heating the floors will be much cooler than the water in the radiator.
For the manufacture of three-way safety valves the following is used:
- steel;
- brass;
- cast iron.
Brass structures are most common when installing home heating systems, while steel and cast iron are more typical for larger industrial installations.
It is also worth paying attention to the explosion safety valve, which can prevent the explosion of flammable gases or coal dust. They are made in such a way that if the substance explodes, only the membrane of the structure is damaged, and the pipeline remains unharmed.
This type of product operates automatically. Depending on the pressure, their There are several types of them:
- with pressure up to 2 kPa;
- up to 40 kPa;
- 150 kPa inclusive.
How to choose the right safety valve
 When choosing a safety valve, there are a huge number of factors to consider. In particular, be sure to take the ambient operating pressure into account. If this pressure is higher than normal, then you need choose a product for 2 bar, which can withstand such operating conditions of the product. In addition, you can choose an option with the ability to adjust the pressure so that you can adjust the required mode and find out the exact parameters, in particular, the nominal diameter.
When choosing a safety valve, there are a huge number of factors to consider. In particular, be sure to take the ambient operating pressure into account. If this pressure is higher than normal, then you need choose a product for 2 bar, which can withstand such operating conditions of the product. In addition, you can choose an option with the ability to adjust the pressure so that you can adjust the required mode and find out the exact parameters, in particular, the nominal diameter.
There are a number of standards regarding the performance of calculations; you can also find special calculation programs on the Internet. You can do without calculations and take a structure with a diameter no less than the diameter of the outlet pipe of your boiler, but such a calculation will not be accurate and cannot guarantee high level safety and productivity.
In general, in order to choose the right product, you should consider the following parameters:
- decide on the type of product;
- with a size so that the pressure in the system does not exceed the permissible limits;
- It is better to choose spring-type products for your home;
- open devices are suitable only if the water goes into the atmosphere, and closed ones - if into the outlet pipeline;
- after calculations, you can determine whether a low-lift valve or a full-lift valve is suitable;
- calculate your budget.
Safety valve prices vary depending on the material and other features. For example, a membrane structure Italian made Can buy for about 4 USD., and brass – starting from 12 USD. There are also some valve models whose cost exceeds $100.
Safety valve installation features
When installing the valve, you must strictly follow all the rules that are listed in the regulatory documentation of the product. Also, the installation must be carried out taking into account the power and operating pressure.
Nowadays, you can increasingly find low-temperature floor and radiator heating systems. The list of control devices includes: mixer taps, safety group, collectors and dirt removers, thermostats, valves, circuit balancing, automatic make-up, return heating. Very important element heating system is the boiler safety group. This group includes: a safety valve for heating, an automatic air vent, and a pressure gauge.
Safety and shut-off valves for the heating system
Mixing taps for heating
High-quality heating regulation is carried out by heating taps, which are located in front of the heating ring. Turning the handle of the three-way tap in a certain way opens the bypass, the pump for heating a private house (pump) draws cooled water into the supply, where it mixes with hot water. This is how the water temperature is regulated. The three-way valve for heating operates flexibly.

Boiler safety group
The boiler safety group (block) consists of a safety valve, pressure gauge and air vent. The installation of these elements is also included in the cost of installing water heating. The pressure gauge shows the pressure, and the air vent removes air from the system.
In case of improper operation or failure of the heating system equipment, a sharp increase in pressure may occur. This can cause the destruction of some elements of the heating system, and in the case of a completely unfavorable development of events, the destruction of the structure and even a threat to human life. That is why every heating or hot water supply system must include a safety valve for heating.
 Boiler safety group
Boiler safety group As noted earlier, the safety valve serves to protect the heating system from excessive pressure. In this case, the most susceptible to such situations are systems with steam boilers. But a similar situation can arise in a system more familiar to us - water heating.
Cases of sudden increase in pressure:
- A sharp increase in water temperature, as a result of which steam appears (usually when draining water from the system);
- Feeding the heating system of a private home with too much water (in case of failure of automatic systems).
In the heating system, the water temperature can reach 90 degrees.
But the filling of the system occurs at a temperature of about 15 degrees. It is obvious that during heating the temperature of the coolant increases and expands in volume. It is to protect the system that such heating control valves are designed. The valve is included in the pipeline fittings, which automatically protect the heating system from excessive pressure due to the fact that part of the coolant is removed from the equipment. Spring valves are most often used; they counteract pressure with the force of a spring.
According to the principle of removing excess coolant volume, safety valves are open and closed.
Open type valves operate without the use of back pressure and remove excess liquid from the heating system. A closed-type heating control valve discharges the coolant into the pipeline, working using back pressure.
 Safety valve
Safety valve In order for the installation of water heating to be done efficiently and reliably, safety devices must be installed correctly. Installation rules are prescribed in regulatory documents, they may vary depending on the power of the equipment and operating pressure.
Basic principles:
- The safety valve in the heating system must be installed on the supply pipe immediately after the boiler. At a certain power level, the two devices cut in and duplicate.
- In systems with hot water supply, the valve is placed at the hot water outlet at the top point of the boiler.
- Installation of a water heating system assumes the absence of various devices between the valves and main pipes. Also, pipes cannot be narrowed to a diameter less than the nominal diameter of the valve.
- Discharge pipes must be connected to a pipeline line of sufficient diameter; they are discharged to a special safe place or sewer network.
The selection of the nominal valve diameter must be made according to methods that have been developed and approved by the relevant authorities. That is why in this case it is necessary to contact specialists. If this is not possible, then there are special programs that calculate the water heating of a private house.
The valves are adjusted to a pressure 15-25% higher than the operating pressure in the system.
Checking the operation of the valve involves forcing it to open; it is advisable to do it regularly. Checking the opening pressure and adjusting it should be done about once a year, just before the heating season begins.
Distribution collectors and slurry collectors
The manifold is a larger diameter pipe, which is designed to equalize the pressure in the pipes. The manifold is placed in the heating distribution cabinet.
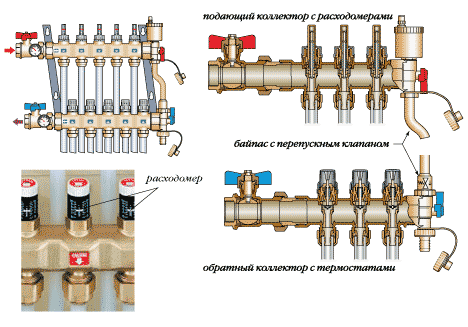 Distributing collectors
Distributing collectors To remove sludge, ball valves are installed into the collectors for heating. There are also special devices– desludge removers. Inside they have mesh surfaces that are arranged like a fan. The sludge that is in the water collides with them, is separated and falls to the bottom of the body and is then taken to a special place.
Thermostats
The thermostat for water heating consists of two elements - a valve (valve) and a thermoelement. The valve serves to regulate heat transfer; it changes the water flow depending on the air temperature. The valve consists of a body and a spool.
 Thermostat
Thermostat The valve capacity is determined by the height of movement of the spool. So, in this case, valves are low-lift and full-lift. In low-lift ones, the lifting height of the spool is equal to 0.05 of the seat diameter. Typically, such valves are used in systems where the liquid medium does not require large throughput. Full lift ones have a spool height higher than 0.25 times the size of the seat diameter. Used in systems with gaseous media.
Along with spring valves, lever-load valves are also used. A lever-load mechanism is a shut-off control valve for heating, where the spool is connected to a lever where a load is hung. The weight can be moved along the entire length of the lever, adjusting the force with which the spool is pressed against the seat.
When the pressure of the medium on the lower plane of the spool is greater than the pressure force of the lever, the valve opens and water from the pipes flows through the discharge pipe.
To equalize the pressure in the system, a reed check valve for heating is used. A special device is also used - a bypass valve in the heating system. The scheme of its operation is the same as that of the safety one, but here the pipe is connected to the return line. As the pressure increases, the bypass valve turns on, transferring water to the return line. To balance the pressure, a check valve is installed for heating.
 Bypass and check valves
Bypass and check valves Mechanism of operation: a check valve in a heating system allows water to flow in one direction, locking it when it moves back. The need for such a device as a gravity check valve for heating is determined by the calculation of hydraulic resistance and pressure.
Other shut-off valves
The heating system uses needle valves. The needle valve for heating has a shutter shape in the form of a narrow cone. It reliably shuts off and regulates the flow of water at high pressures.
The phrase in the name of the mechanism indicates what function it should perform in water circuits. Indeed, a safety valve for heating (shut-off valves) serves to relieve unexpected loads that may arise under certain circumstances, as well as to regulate the water flow in the pipes. But it is installed in different places, although its purpose remains the same.
Types of safety valves
Types of check valves for bypass or boiler

- Coupled brass fuses They are equipped with threads on both sides and an EPDM gasket on the input side, and the mechanism itself operates on a spring that holds the rod, which, at a certain pressure, is recessed, opening the passage. Any pressure from reverse side only strengthens the blocking. Considering the simplicity of such a fuse, the price for it is rather symbolic, but it lasts quite a long time, since it always undergoes pressure testing after assembly.
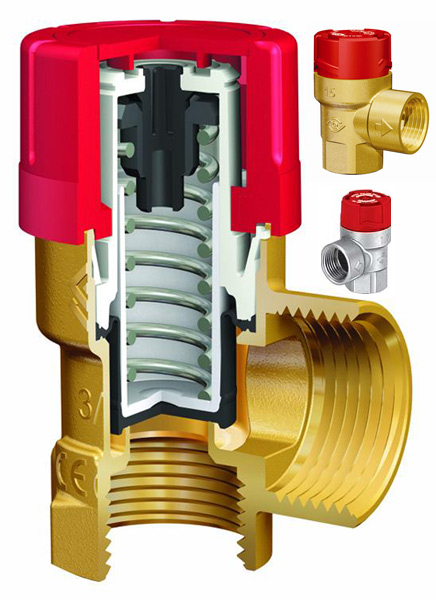
- But, unlike a conventional valve, there are pressure relief devices, like what you see in the photo above. Such a mechanism, as a rule, is also made of brass, with a stainless steel spring and a rod plate made of heat-resistant plastic, and is mounted in the circuit after the circulation pump.
- In the cut image shut-off valves the principle of its operation is visible - water presses on a plastic plate, which, in turn, compresses the spring, opening the passage. But if the pressure reaches a critical point (20 bar), then the plate is pressed against the safety rod and it opens the exit to the outside. Maximum operating temperature for this mechanism - 120⁰C.

- In addition to the circulation pump, a heating bypass valve can also be installed to tanks with high pressure , for example, it could be an electric boiler. Its operating principle will remain the same, only there is a device for draining water. This is done using a flag, which moves the rod and clears the passage.
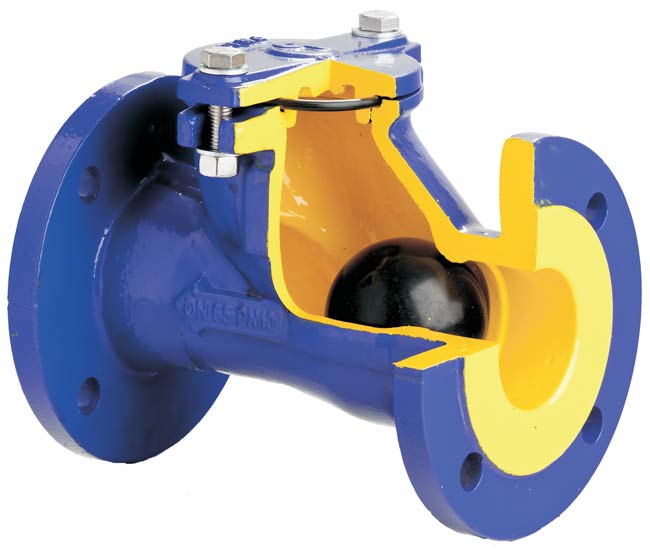

- Such reverse devices are most often used in sewerage systems to protect against backflow pressure. This can happen during the snowmelt or heavy rain season, when groundwater fill the city sewer system and the water level rises above the drain pipes.

- The essence of the lifting locking device is that when the water supply presses on the valve, it rises and allows the flow to pass. If the pressure drops, the rod is lowered onto the seat and flow return is eliminated. Such a check valve in a heating system is most often used in industrial facilities and for centralized boiler houses.
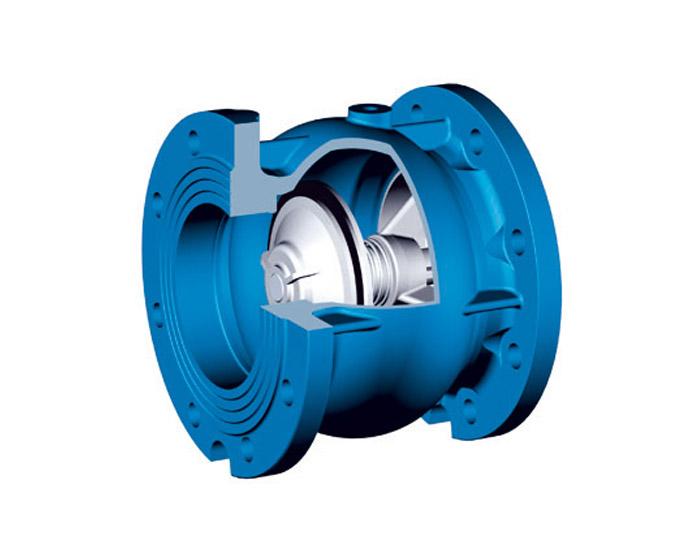

- In such mechanisms the locking element is a disk that is perpendicular to the flow and moves along the axis. The mechanism can be made either as a coupling or with flange mountings. Used for systems with low pressure and relatively clean coolant.
Advice. Check valves can be spring-loaded (spring-loaded), where the flap is returned into place due to the pressure of the spiral. Or springless, where the damper returns under the pressure of the mass itself. When choosing, you should always take into account the degree of water contamination, since without force the stem may not close due to blockages.
Three way valves

- If we consider a three-way valve for heating, then its operating principle, as well as its purpose, is somewhat different from conventional safety devices. The need for such a mechanism in heating circuits is determined by the need for cooling. Such units can be with manual mode switching or with a servo drive powered from a 220V network.

- The three-way valve is quite simple in design and has one inlet and two outlets, the flow into which is regulated by a damper. The damper can be either a rod or a ball, which, when rotated, redirects the flow into one of the holes. Such fittings also belong to the category of safety valves, since they are installed on low-temperature circuits, for example, where radiators are adjacent to a “warm floor” and at the same time operate from one source (boiler).
- The fact is that the instructions for combined heating systems do not provide for different heaters, so the water enters the circuit the same and in order to reduce its heating, the supply pipe is fed from the return pipe (“return”). Thus, the water temperature is lower than for radiators.
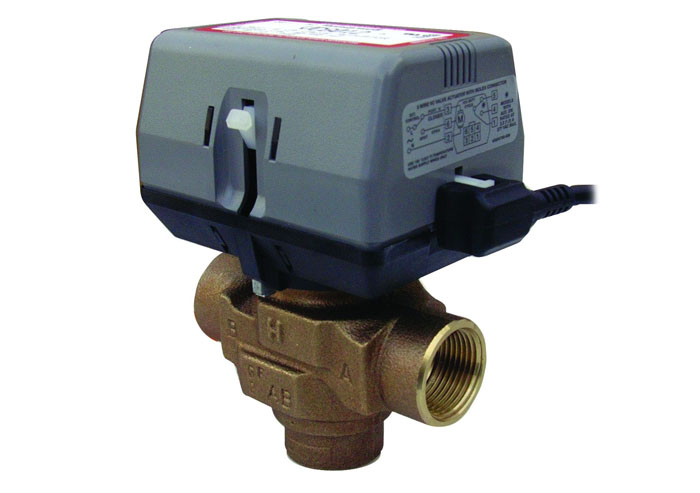

- Mixing of the coolant can occur automatically and for this, sensors are installed on the low-temperature circuit, signaling servo and motivating him to action. When purchasing such a mechanism, you should not forget that the servo drive itself may be complete with the valve, but you can also purchase it separately and install it yourself by choosing the manufacturer that suits you.
- Such a device, complete with electronics, can be very expensive, but, to paraphrase the well-known saying about the sheepskin, we can say that an expensive three-way mixing valve with a servo drive is worth the money, or the money spent on it. By using electronic shut-off valves, you will save yourself from the need to constantly monitor the system and will be able to leave the house with the heating on for a long period.
Advice. Three-way valves can be made of cast iron, steel or brass and are desirable for use in systems with varying flow rates and pressures. Thus, steel and cast iron devices are better suited for centralized and industrial facilities, and brass is very effective for home heating systems.
