In order for the house to be dry and warm when performing thermal insulation work, it is important to correctly determine the dew point. If the calculation was initially performed incorrectly, the walls will begin to get wet, traces of condensate will appear. Moreover, the error will become noticeable only after a few years. It will be extremely difficult to fix something, and therefore all the work will have to be done again.
What is dew point?
This parameter is numerically equal to the temperature at which water vapor begins to condense from the cooled air, turning into dew. Its value can vary along the thickness of the wall with temperature fluctuations inside and outside the building. If the temperature inside is maintained at the same level, and it starts to get colder outside, the dew point will begin to move closer to the inner wall.
The temperature at which steam begins to condense is affected by the temperature and humidity of the air. So, at an air temperature of + 20 °C and a humidity of 50%, dew will fall on a surface cooled to +12.9 °C. To check this, it is enough to bring an object cooled below +12.9C into the room. There will definitely be condensation on it. If, on the contrary, you open the refrigerator, warm air will begin to flow into it, from which dew will fall. Outwardly, it will look like fog coming out of the refrigerator.
There is also a place in the wall of the house where steam will condense if it is very cold outside. With insufficient wall thickness and cooling of its surface to a certain level, dew will begin to appear inside the room. As a result, the wall will constantly get wet and will soon be covered with mold.
That is why, when insulating, it is imperative to calculate the dew point, taking into account the highest and lowest values of humidity and temperature, both inside and outside. This will allow you to find out how it will shift in space with changes in temperature and humidity. Based on the obtained values, it will be possible to calculate the minimum wall thickness at which there will be comfortable conditions inside the house.
How to find the place you are looking for?
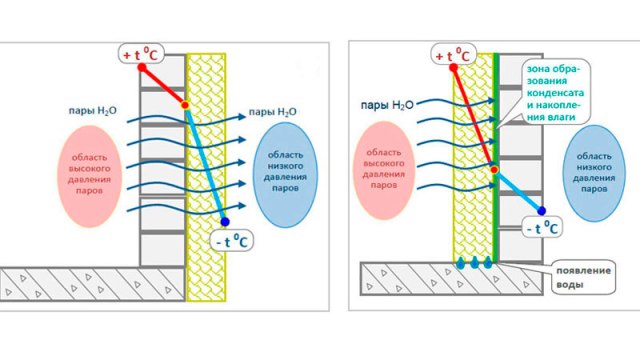
Where exactly the steam will condense depends largely on the location of the heater. This is especially important if the insulation was made from the inside.
The position of the dew point will directly depend on weather conditions. In the absence of significant temperature fluctuations in the outside air, condensation will form closer to the outer surface of the wall. Inside the building, it will be quite comfortable.

In the event of a sharp cold snap, the desired place will slowly begin to shift inward. This can lead to a gradual saturation of the interior with condensate and wetting of the walls.
In this case, one should correctly approach the choice of heat-insulating material and its thickness in order to prevent the walls from getting wet. If the thermal insulation of the walls outside is done correctly, the dew point will be inside the insulation.

If the installation technology is violated or the thickness of the heat-insulating material is insufficient, then it will be extremely difficult to reduce heat loss.
When frost increases inside the building, humidity can increase. It is also possible that the walls get wet.
The desired place for insulation from the inside will be located between the middle of the wall and the insulation. This is not the best option, since with high humidity and a sharp decrease in air temperature, condensate will begin to form at the junction of the insulation and the wall.
As a result, the destruction of the insulated surface and the heat-insulating material may begin. This option at high humidity is possible only in the case of installing a heating system that can maintain the temperature throughout the house at the same level.
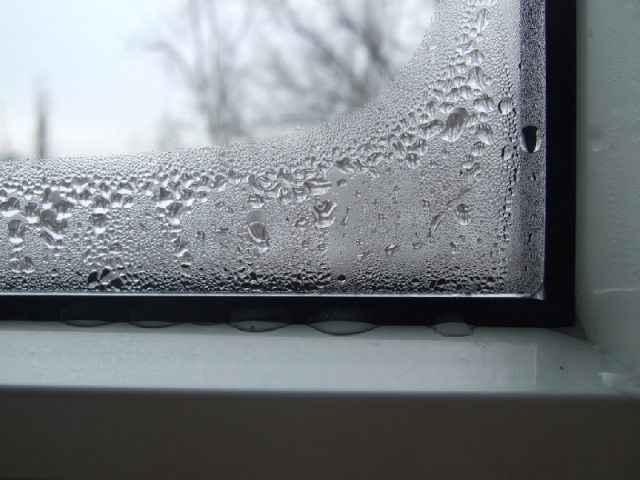

If, when performing thermal insulation work from the inside, the climatic features of a particular region were not taken into account, it will be extremely difficult to eliminate the problems that have arisen. The only possible way out of this situation is to re-insulate the walls. It should be noted that the internal insulation, according to experts, is significantly inferior to the external one.
We carry out the calculation
When determining the required value, several factors should be taken into account at once:
- temperature inside and outside the house;
- air humidity.
Temperature and relative humidity
The value depends on the location of the building. In most cases, we will talk about 20 - 22 ° C. For those who live in areas where the five-day period is the coldest, that is, it happens -31 ° C and lower, the indicated value will be 21-23 ° C.

The allowed value is slightly different. For cold regions, it will be 20 - 24 ° C. For the middle band, the temperature range will expand to 18 - 24 ° C. When calculating, it is usually taken in the first case 20 ° C, in the second - 22 ° C.
Permissible relative humidity ranges from 35–60%. For calculations, you can take 50-55%.
We are looking for a table value
To find the desired value, you should use a special table in which the condensation value is presented depending on temperature and humidity. To do this, having determined the temperature and humidity, you can find the desired value at the place of their intersection. So, if the humidity is assumed to be 55% and the temperature is 21°C, the dew point is 11.6°C. This means that where the wall cools down to 11.6 °C, condensation will form.
To get a more accurate figure, you can determine the value of condensation from real data. To do this, you should acquire the following tools:
- conventional thermometer;
- hygrometer;
- non-contact thermometer. In its absence, you can use the usual.

The search for a value should start with measuring the air temperature at a distance of 60 cm from the floor surface. A larger offset from the floor surface will result in incorrect data. Measurements in this case are often carried out by placing the thermometer on the table.
After that, the humidity in the room is measured using a hygrometer. This should be done in the same place where the temperature was measured. The search for the condensation value is carried out in the same sequence as described above.
Is insulation necessary?
Sometimes it can be difficult to determine how much thermal insulation work is needed. Before proceeding with the insulation of the walls, it is worth using a special non-contact thermometer to find the temperature of the surface located at a distance of approximately 60 cm from the floor plane.
In the absence of such a measuring tool, you can use a conventional thermometer. To do this, wrap the thermometer with a thin cloth and put it on the surface, the temperature of which is to be determined. In a quarter of an hour it will be possible to take readings.

Now we have to compare the table value of condensation and the surface temperature. If the difference is more than 4 degrees, we can safely say that the room has high humidity, and the dew point is inside.
It will be extremely difficult to deal with the problem on your own. It is advisable to seek help from specialists who can correctly calculate the optimal thickness of the heat-insulating material and its characteristics.
Determine the place of condensation
In order to perform the calculation, you need to know:
- coefficients of thermal resistance of the wall and insulation, λ1 and λ2, W/(m K);
- thickness of the wall and insulation, h1 and h2, m;
- air temperature inside the house, t1, °С;
- air humidity, %;
- dew point, °С;
- temperature outside the building, t2, °С.
Before proceeding to the calculation, we assume that the temperature change will be linear over the thickness of all layers. It is necessary to find the temperature at the point of contact between the wall and the insulation. After that, it will be necessary to build a graph that reflects the change in temperature across the thickness of the wall. The constructed graph will help you find the desired point.
![]()
To do this, you should find the ratio of the value of the thermal resistance of the wall and insulation. Using a special formula, it will be possible to find the temperature at the boundary of the layer. Knowing the temperature on one and the other side of the layer, it will not be difficult to build a line graph. Using it, it will be possible to track the temperature change in the entire thickness of the wall in order to understand exactly where the condensate will form.
To perform the calculation, let's assume that we have a reinforced concrete wall h1=36 cm, insulated with foam plastic h2=10 cm thick. For reinforced concrete, the coefficient of thermal resistance is λ1=1.7 W/cmK. For foam plastic, this indicator λ2 = 0.04 W / cmK. Inside the house, the temperature is t1= +20 degrees, outside - t2= -10 degrees. We will take the same air humidity inside and outside - 50%. According to the table, the condensation value will be 9.3 degrees.
To find the thermal resistance of the wall and the insulation, it is necessary to find the ratio of their thickness and the coefficient of thermal resistance h / λ. We get for the wall h1 / λ1 = 0.36 / 1.7 = 0.21 W / m²K, insulation h2 / λ2 0.1 / 0.04 = 2.5 W / m²K.
Hence, at the boundary of the layer, the temperature will be t1-T=20-2.52=17.48 degrees.
To find where the desired place will be, you should build an approximate graph that characterizes the temperature drop across the thickness of the wall by drawing a straight line through two points. In the place where the temperature is 9.3 degrees, and condensation will form.
Analyzing the resulting graph, it is important to understand whether the place of condensation will be in the insulation or not. In this case, even with a significant deterioration in weather conditions, it will be possible to avoid unwanted wetting of the wall. If it turns out to be outside the layer of heat-insulating material, then it's time to think about the adequacy of the thickness of the insulation.
If at the moment it is not possible to improve the thermal insulation of the walls, then the only way out may be to heat the room. By heating the air from the inside, it will be possible to shift the condensation point towards the street. As a result, it will be much more comfortable inside the building.
